Benefits Corner
Benefits Corner features stories on what life events qualify for changes to employee benefits. Also featured are stories to help you achieve financial wellness and an understanding of diabetes.
Qualifying life events…

What You Need to Know
Did you know that because your benefits are deducted on a pretax basis, there are set IRS limits of when an employee may make changes to their benefits outside of the new hire and/or open enrollment periods?
An eligible employee may only change benefit elections outside of new/open enrollment periods if they experience a qualifying life event such as, but not limited to, a birth, adoption, marriage or divorce.
Employees must notify the Benefits Department with 31 days of the life event occurring to qualify for changes.
For more detailed information, please review the "New Hire/Open Enrollment Guide" available on the EIC and through the enrollment website.
Enjoy Financial Wellness
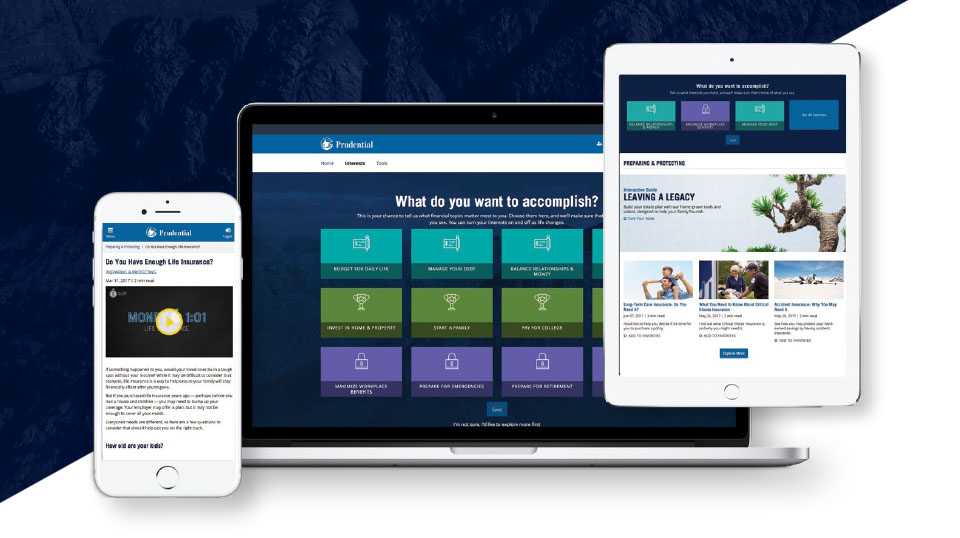
Financial wellness is the peace of mind you feel when you’ve balanced saving and spending … planning for the unexpected and for tomorrow.
How do you achieve it? That’s what the Financial Wellness Center is for.
The Financial Wellness Center contains:
- Engaging articles
- Short videos
- Interactive tools
All of which can help you achieve your financial wellness goals. Register online and personalize your experience based on your most important goals. And the Center’s content becomes more relevant the more you use it.
Visit it today: www.prudential.com/saia
Group Insurance coverages are issued by The Prudential Insurance Company of America, a Prudential Financial company, Newark, NJ.
©2019 Prudential Financial, Inc. and its related entities. Prudential, the Prudential logo, the Rock symbol, and Bring Your Challenges are service marks of Prudential Financial, Inc. and its related entities, registered in many jurisdictions worldwide.

Health Tip: Understanding Diabetes

What is diabetes?
A condition in which the pancreas is unable to process sugar effectively, leading to increased levels of glucose in the blood stream. Diabetes is a chronic condition that can be managed by everyday choices.
Type 1 diabetes is due to an autoimmune process that destroys the cells in the pancreas that make insulin. It is always treated with daily administration of insulin. Type 1 diabetes affects about 5% of the people with diabetes.
With type 2 diabetes, your body cannot properly use insulin (a hormone that helps glucose get into the cells of the body). This results in blood glucose levels being higher than normal. Glucose, commonly known as sugar, is a source of energy. Foods that contain carbohydrates, such as fruit, bread, pasta and rice are common sources of glucose. When we eat these foods, they are broken down into simple sugar and then absorbed in our bloodstream. If your body is unable to process excess sugars effectively, your blood glucose levels rise to unhealthy levels. Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes and can be treated with healthier lifestyle choices, oral medications, non-insulin injections and/or insulin.
Having pre-diabetes means your blood glucose (sugar) levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes. Pre-diabetes may lead to heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. Pre-diabetes may often be reversed by making healthier lifestyle choices.
Why is it important to understand diabetes [1]?

Diabetes signs and symptoms
- Fatigue
- Frequent urination
- Increased thirst and hunger
- Weight loss
- Blurred vision
- Slow healing of wounds or sores
If you have any of these signs and/or symptoms you should speak to your healthcare provider
Diabetes risk factors
Factors you cannot change:
- Age
- Gender
- Race
Factors you can impact:
- Weight
- Inactivity
- Blood Pressure
- Cholesterol
Managing diabetes/reducing your risk [2]
- Eat healthier by including a diet with lots of non-starchy vegetables; whole grain foods, lean cuts of meat, poultry, and non-fat dairy products. Include fatty fish (salmon, trout, sardines) 2-3 times per week.
- Get daily exercise by aiming for 30 minutes of moderate physical activity on most days of the week.
- Maintain or obtain a healthy weight defined as a body mass index (BMI) measurement between 18.5 - 24.9.
- Monitor blood glucose regularly. Most people with diabetes should aim for an A1C of 7 or less.
- Take medications as prescribed.
- Don’t smoke.
- Learn ways to lower your stress.
- Obtain routine care with your healthcare provider.
Based on a study by the Diabetes Prevention Program, a moderate weight reduction of 5 percent can help reduce the development of type 2 diabetes by 58 percent. [3]
[1] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/library/socialmedia/infographics.html
[2] American Diabetes Association, http://www.diabetes.org/living-with-diabetes/treatment-and-care/blood-glucose-control/a1c/
[3] Diabetes Prevention Program Outcome Study, https://dppos.bsc.gwu.edu/web/dppos/dpp
M57233-F 5/19
©2019 United HealthCare Services, Inc.




